Comprehensive Guide to Solar PV Systems: From Working Principles to Key Components
2025-05-14
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems are rapidly growing worldwide as a key clean energy solution. However, many people are unfamiliar with how they work and their critical components. This article provides an in-depth analysis of how solar PV systems are structured and operate, with detailed explanations of key equipment such as combiner boxes, over/under-voltage protectors, isolator switches, solar connectors, fuses, and molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs).
1. How Is a Solar PV System Structured?
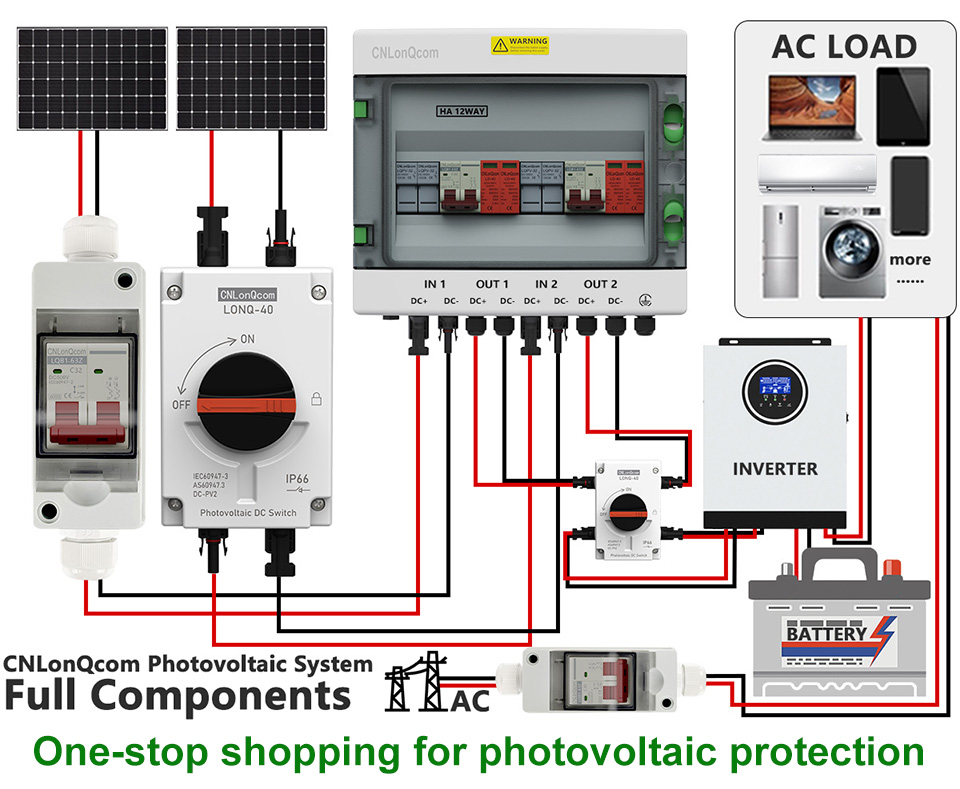
The core objective of a solar PV system is to convert sunlight into electricity and safely deliver it to the grid or energy storage. A complete system typically includes the following components:
Solar Panels (PV Modules) → Absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC)
Combiner Box (LQX/LQT Series) → Combines currents from multiple solar panels
Inverter → Converts DC to alternating current (AC)
Power Distribution & Protection Devices (fuses, circuit breakers, isolator switches, etc.) → Ensures system safety
Energy Storage System (Optional) → Stores excess electricity (e.g., lithium batteries)
Grid or Load → Supplies power to homes, businesses, or the grid
2. How Does a Solar PV System Work?
(1) Photovoltaic Effect & Power Generation
Sunlight strikes solar panels (PV modules), and the silicon semiconductor material absorbs photons, generating direct current (DC).
A single panel typically produces 30V-50V (DC), with current depending on sunlight intensity and panel efficiency.
(2) Current Combining (Combiner Box)
Multiple panels are connected in series or parallel, and the combined current flows into a PV combiner box for centralized management.
The combiner box includes fuses, surge protection (SPD), and current monitoring to prevent overloads or short circuits.
(3) DC Power Distribution & Protection (Fuses, Isolator Switches, MCCBs)
Fuse (LQPV-32 Series): Prevents excessive current from damaging equipment.
Isolator Switch (LONQ-40 Series): Manually disconnects circuits for maintenance.
Molded Case Circuit Breaker (LQM1/M3 Series): Provides overload and short-circuit protection (e.g., 1000V DC-rated MCCBs).
(4) Inverter Conversion (DC → AC)
DC power enters the inverter, converting it into 220V/380V AC for household or industrial use.
Grid-tied systems feed excess power back to the grid, while off-grid systems store it in batteries.
(5) Over/Under-Voltage Protection (AVP 2P/4P Series)
When grid voltage fluctuates, the over/under-voltage protector automatically cuts off power to prevent equipment damage.
(6) Wiring & Connections (Solar Connectors)
MC4 solar connectors are the industry standard, ensuring waterproof, corrosion-resistant, and high-current transmission (e.g., 30A/1000V).
3. Key Components of a Solar PV System
(1) PV Combiner Box
Function: Combines multiple solar panel strings and provides protection.
Key Components:
Fuses (overcurrent protection)
Surge Protection Device (SPD) (lightning protection)
Current/voltage monitoring (optional smart features)
(2) Over/Under-Voltage Protector (OVP/UVP)
Function: Monitors grid voltage and disconnects power if voltage is too high (>270V AC) or too low (<170V AC).
(3) DC Isolator Switch
Function: Manually disconnects DC circuits for safe maintenance.
Common Types:
Rotary isolator switches (suitable for outdoor use)
Circuit breaker-type isolators (with integrated protection)
(4) Solar Connectors (MC4 Standard)
Key Features:
Waterproof, UV-resistant, high-temperature tolerance
Rated current: 30A
Rated voltage: 1000V DC
(5) PV Fuses (gPV/gR Series)
Function: Protects PV arrays from short circuits and overloads.
Differences from standard fuses:
High voltage rating (DC 1000V+)
High breaking capacity (can interrupt large fault currents)
(6) Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB for Solar)
Function: Provides overload and short-circuit protection for DC systems.
Typical Specifications:
Rated voltage: DC 1000V
Rated current: 32A-250A
4. Applications of Solar PV Systems
Residential Rooftop Solar (5kW-10kW, with storage)
Commercial & Industrial PV Plants (50kW-1MW, grid-tied)
Off-Grid Solar Systems (Remote areas, battery-based)
Agrivoltaics (Solar + Agriculture Integration)
5. Future Trends: Smarter & More Efficient Solar Systems
Smart Monitoring: Real-time tracking via mobile apps (e.g., power generation, fault alerts).
Solar + Storage Integration: Hybrid systems like Tesla Powerwall.
Microinverters: Optimizes each panel individually for higher efficiency.
Conclusion
Solar PV systems operate through the process of PV modules → combiner box → inverter → power distribution → grid/storage, with critical components like combiner boxes, fuses, isolator switches, connectors, and MCCBs ensuring efficient, safe, and stable performance.
If you're considering a solar installation, choose CNLonQcom high-quality PV components + professional protection devices to maximize system lifespan and power generation efficiency!
🔋 Let’s Discuss: What aspect of solar PV systems interests you the most?