Top 10 Facts About Lead Batteries You Need to Know!
Lead batteries have been an essential source of power for various applications since their invention in the mid-19th century. Despite the age of this technology, lead batteries continue to play a crucial role in our daily lives, from powering vehicles to supporting renewable energy systems. Understanding the fundamentals of lead batteries is vital, especially as we seek more sustainable energy solutions and ways to reduce our carbon footprint.
In this overview, we will explore ten key facts about lead batteries that highlight their importance, efficiency, and environmental impact. These facts will shed light on how lead batteries operate, their advantages over other types of batteries, and their longevity in various applications. Whether you are a curious consumer or an industry professional, this knowledge will enhance your understanding of lead batteries and their ongoing relevance in today’s energy landscape.
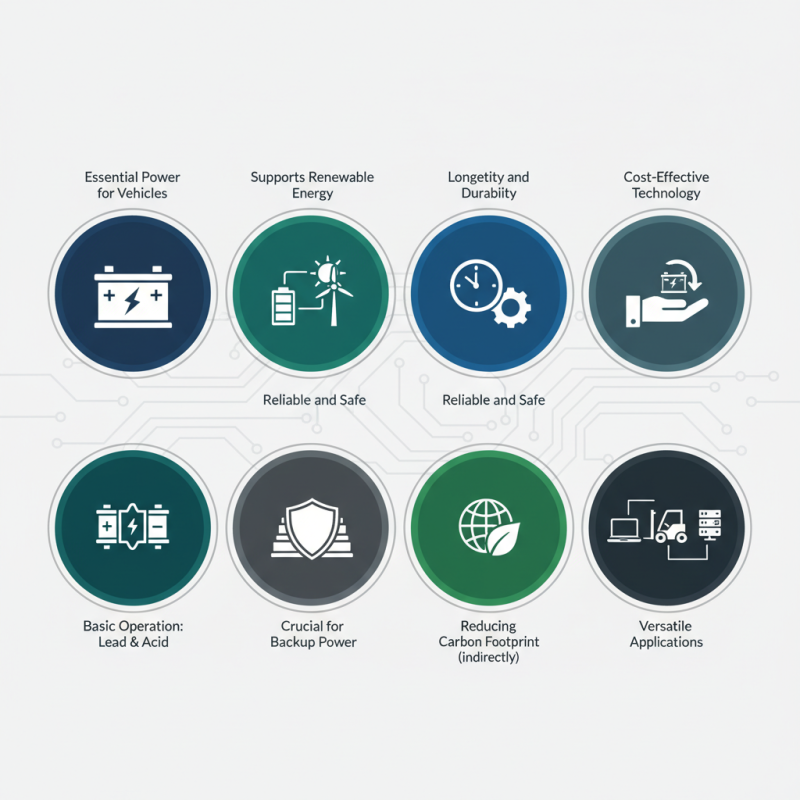
History and Development of Lead Batteries
The history of lead batteries dates back to the mid-19th century when French engineer Gaston Planté invented the first rechargeable lead-acid battery in 1859. This innovation marked a significant breakthrough in energy storage technology, enabling the efficient harnessing of electrical energy. The lead battery's design, utilizing lead and sulfuric acid, has since been adapted and refined, making it a prominent choice for energy storage in various applications, including automotive and stationary power systems.
As the technology evolved through the decades, lead batteries became vital for electrical systems, particularly during the rise of automobiles in the early 20th century. Their ability to provide a reliable source of power for starting engines, as well as for lighting and ignition systems, cemented their importance in the automotive industry. The lead battery's robust performance and longevity have contributed to its enduring popularity, even as newer battery technologies emerge.
Tips: When considering lead batteries for your needs, it's essential to understand their maintenance requirements. Regularly checking the electrolyte levels and ensuring proper charging can significantly extend their lifespan. Additionally, for those exploring recycling options, lead batteries are highly recyclable, making them an environmentally friendly choice when disposed of correctly. Always adhere to local recycling guidelines to ensure safe and proper disposal.
Top 10 Facts About Lead Batteries You Need to Know! - History and Development of Lead Batteries
| Fact Number | Fact | Year Introduced |
Key Contributor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lead batteries were first invented in 1859. | 1859 | Gaston Planté |
| 2 | They are the oldest type of rechargeable battery. | N/A | N/A |
| 3 | Lead batteries are highly recyclable, with a 99% recycling rate. | N/A | N/A |
| 4 | They are commonly used in vehicles, including cars and trucks. | N/A | N/A |
| 5 | The lead-acid battery design includes positive and negative plates. | N/A | N/A |
| 6 | Lead batteries can deliver high surge currents, ideal for starting engines. | N/A | N/A |
| 7 | They have a relatively low energy density compared to other batteries. | N/A | N/A |
| 8 | Lead batteries can be damaged by deep discharges, reducing lifespan. | N/A | N/A |
| 9 | They have reliable performance in a wide range of temperatures. | N/A | N/A |
| 10 | They contribute significantly to the renewable energy sector by storing solar energy. | N/A | N/A |
Basic Components and Chemistry of Lead Batteries
Lead batteries, also known as lead-acid batteries, are composed of several key components that work together to store and provide electrical energy. The fundamental elements include lead (Pb) dioxide for the positive plate, sponge lead for the negative plate, and a sulfuric acid (H2SO4) electrolyte that facilitates the chemical reactions necessary for energy storage and release. During discharge, lead dioxide and sponge lead react with the sulfuric acid to produce lead sulfate (PbSO4) and water, releasing energy in the process. This cycle reverses during charging, where an external electrical current restores the original materials.
Research from the International Lead Association highlights that lead batteries are highly recyclable, with over 95% of their components being recoverable. This not only minimizes environmental impact but also makes them a cost-effective energy solution. Furthermore, according to a report from the Battery Council International, the global market for lead-acid batteries is estimated to be valued at over $60 billion, primarily driven by their extensive applications in automotive, industrial, and renewable energy sectors.
Tips: Consider regular maintenance of your lead battery systems to enhance their lifespan. Monitoring electrolyte levels and ensuring proper charging practices can help maximize performance. Additionally, be aware of signs of deterioration, such as reduced capacity or swelling, as these can indicate the need for professional assessment or replacement. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your lead batteries operate efficiently and sustainably over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Lead Batteries
Lead batteries, widely used in various applications, come with distinct advantages and disadvantages that merit consideration. One of the primary advantages is their cost-effectiveness. Lead batteries are relatively inexpensive to produce compared to other battery technologies, which makes them a popular choice for automotive and backup power systems. Additionally, they offer reliable performance and a well-established recycling infrastructure, allowing them to be reclaimed at a high rate. This long history of usage has led to considerable knowledge regarding their maintenance and care, making them a practical choice for many consumers.
On the flip side, lead batteries are not without their drawbacks. One significant disadvantage is their weight; they tend to be heavier than other battery types, which can be a limitation in applications where weight is critical, such as in electric vehicles. Moreover, lead batteries have a relatively lower energy density, meaning they store less energy for their size compared to lithium-ion batteries or other alternatives. They also exhibit a shorter lifespan, particularly if not maintained properly, which can lead to increased costs over time. Lastly, while the recycling process is established, the environmental impact of lead, particularly if batteries are not disposed of correctly, remains a serious concern.
Applications of Lead Batteries in Various Industries
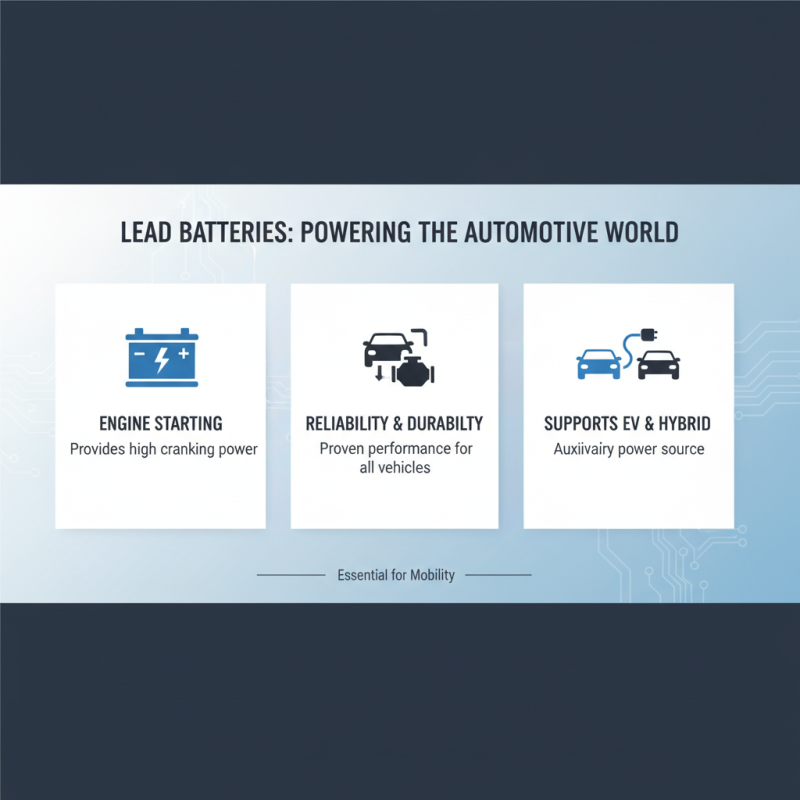
Lead batteries, known for their durability and reliability, find extensive applications across various industries. One significant area is the automotive sector, where they power vehicles, providing the necessary cranking power for engine starts. Their ability to quickly provide high bursts of energy makes them ideal for this purpose. Not only do they serve in traditional gasoline engines, but they also support hybrid and electric vehicles by functioning as auxiliary power sources.
Another crucial application is in the telecommunications industry. Lead batteries are widely used as backup power sources for phone networks and data centers, ensuring continuous operation during power outages. Their robustness and reliability make them a preferred choice for maintaining power quality in critical communication systems.
**Tips:** When considering lead batteries for your application, make sure to assess factors such as energy needs and cycle life. Regular maintenance can significantly extend their lifespan. Additionally, when recycling old lead batteries, ensure they are handled by certified facilities to promote environmental sustainability.
Recycling Processes and Environmental Impact of Lead Batteries

The recycling processes for lead batteries are crucial for minimizing environmental impact while maximizing resource recovery. Lead-acid batteries, prevalent in various applications, have an impressive recycling rate of approximately 99%. According to the International Lead Association (ILA), around 80% of the lead used in new batteries comes from recycled sources, which significantly curbs the need for virgin lead extraction and its associated environmental degradation.
The recycling process typically involves the mechanical separation of battery components followed by smelting to extract lead and other valuable materials. A comprehensive study conducted by the Battery Council International (BCI) revealed that for every ton of lead sent for recycling, an estimated 1.3 tons of carbon dioxide emissions are avoided compared to new lead production. This highlights that efficient recycling not only conserves natural resources but also mitigates greenhouse gas emissions, contributing positively to efforts against climate change. Through stringent regulations and advancements in recycling technology, the lead battery industry continues to improve its environmental footprint, ensuring a sustainable pathway for energy storage solutions.
Related Posts
-
How to Choose the Right Lead Battery for Your Needs: A Complete Guide
-

Unlocking the Benefits: Why Rechargeable Sealed Lead Acid Batteries Are the Future of Power Storage
-

Unleashing the Power: Exploring the Future of Eco-Friendly Batteries & More Innovations
-

Why Lawn Mower Batteries Are Essential for Every Gardener's Toolkit
-

Unveiling Battery Acid Innovations at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Revolutionizing Yard Care: How Lawn Batteries are Leading the Charge Towards Eco-Friendly Landscaping
