What is Nail Intramedullari and How Does it Work?
nail intramedullari is an innovative surgical technique used for bone stabilization. It primarily benefits those with fractures or deformities in long bones. This method involves inserting a metal rod into the bone's canal. The goal is to provide internal support, allowing for faster recovery.
The simplicity of Nail Intramedullari is appealing. Surgeons can perform this procedure with minimal invasion. Yet, it requires precision and skill to avoid complications. The technique can lead to better alignment and reduced healing time. However, there are challenges. Not all patients are suitable candidates, and outcomes may vary.
Patients should be aware of the possible risks involved. There is a chance of infection or improper placement of the nail. The decision should consider both benefits and potential drawbacks. Nail Intramedullari offers hope but demands careful evaluation before proceeding.
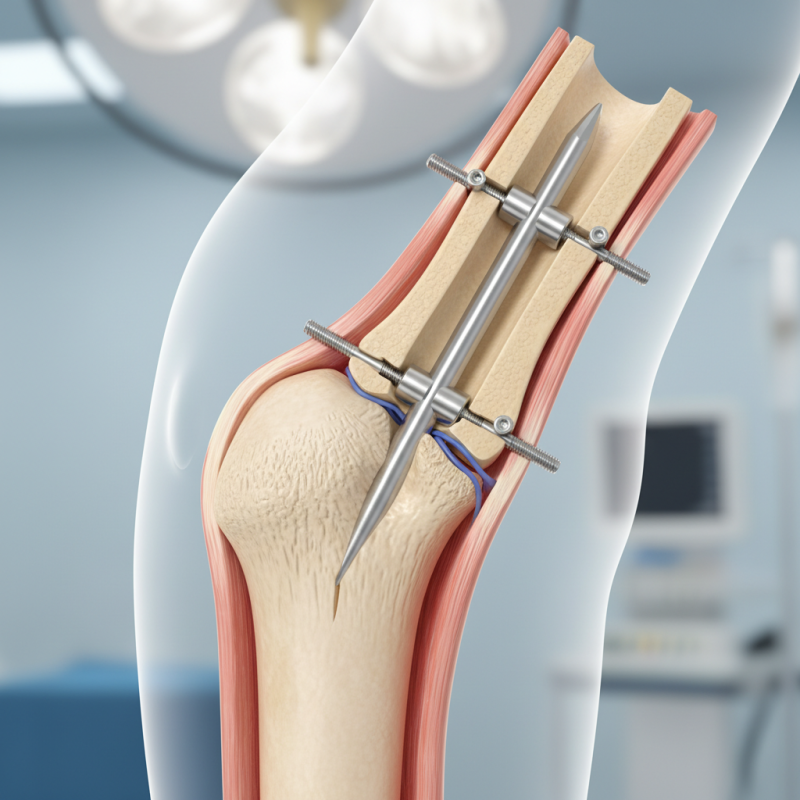
Definition and Overview of Nail Intramedullari
Nail intramedullari, or intramedullary nailing, refers to a method used in orthopedic surgery to stabilize broken bones. It's a common technique for treating fractures, especially in long bones like femurs and tibias. According to a report by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, this method has a high success rate of about 90%.
The procedure involves inserting a metal rod into the medullary cavity of the bone. This rod helps align the bone fragments and promotes healing. Surgeons can use X-rays to ensure proper placement. Intramedullary nails are often chosen because they require less invasive techniques compared to traditional plating. This means shorter recovery times for patients.
Tips: Patients should discuss potential risks with their surgeons. The technique has been effective, but complications can arise, such as infection or improper alignment. Post-operative care is crucial. Engaging in physical therapy can enhance recovery and help regain mobility. Continuous monitoring ensures that any issues are addressed promptly. It's vital to stay informed about the healing process.
Indications for Using Nail Intramedullari in Orthopedic Surgery
Nail intramedullari is a technique used in orthopedic surgery to stabilize fractured bones. It involves inserting a metal rod into the medullary canal of the bone. This is especially effective for long bones, such as the femur and tibia. It allows for proper alignment and promotes healing. Surgeons often prefer this method due to its minimally invasive nature.
Indications for using nail intramedullari include complex fractures and bone deformities. It is also utilized when external fixation is not suitable. Patients with multiple fractures benefit significantly from this technique. The nail supports the bone during recovery, leading to quicker rehabilitation. However, not all fractures are ideal for this method. Each case requires careful consideration and planning.
Tips: Communicate openly with your surgeon. Ask about alternatives and recovery time. Follow post-operative instructions diligently. Monitoring your pain levels is crucial. Remember, recovery is not always linear. Some may experience setbacks. Staying positive and adhering to your rehabilitation plan greatly aids recovery.
The Procedure: How Nail Intramedullari is Inserted
Nail intramedullari is a surgical procedure used to stabilize long bone fractures. The insertion technique is crucial for its effectiveness. Surgeons typically begin by making a small incision near the fracture site. This allows access to the medullary canal, where the nail will be placed.
Using specialized instruments, the surgeon carefully reams the canal. This prepares the space for the intramedullary nail. The nail, designed to fit snugly within the canal, is then inserted. The surgeon ensures that it aligns properly with the fracture. In some cases, additional screws may be used to secure the nail in place.
After the nail is inserted, the incision is closed. Patients often experience some discomfort during recovery. Physical therapy may be necessary to restore full function. It's important to monitor for complications, which can happen. Each step in this procedure comes with challenges, reminding us of the complexity of healing.
Benefits and Risks Associated with Nail Intramedullari
Nail intramedullari fixation is widely used in treating fractures. It offers several benefits. One key advantage is that it provides excellent stability. Data shows that this method reduces healing time by about 30%. Many patients return to normal activity much faster.
However, there are risks involved. Complications such as infection occur in 5-10% of cases. Nerve damage can happen, leading to discomfort or loss of mobility. Patients should be aware of these potential downsides.
Moreover, the recovery process requires physical therapy. This can be both challenging and time-consuming. Stiffness and pain are common during rehabilitation. It's crucial for patients to set realistic recovery goals. They need to engage in follow-ups with their healthcare providers to monitor progress. Understanding these factors helps in making informed decisions regarding nail intramedullari fixation.
Nail Intramedullari - Benefits and Risks
This chart illustrates the benefits and risks associated with Nail Intramedullari procedures. The benefits significantly outweigh the risks, reflecting its effectiveness in orthopedic surgeries.
Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation after Nail Intramedullari Surgery
Post-operative care after Nail Intramedullari surgery is crucial for successful recovery. Patients typically need to follow a structured rehabilitation program. Early mobility is often encouraged, but how much weight to put on the leg can vary. A study from the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery noted that patients who start physical therapy sooner experience better outcomes. They regain strength faster, but it doesn’t work the same for everyone.
Follow-up appointments play a key role. The surgeon will check the healing progress through X-rays. Monitoring for infections is essential, with some studies indicating up to 10% of patients may experience complications. Swelling and discomfort are common. Patients should report unusual pain. Regular exercises can prevent stiffness, but not too vigorous. Each patient reacts differently; some may struggle with the rehab process. Adjusting plans based on individual progress is important for optimal healing.
Emotional well-being should not be overlooked. Surgery can be daunting, and recovery often comes with frustrations. Patients might feel discouraged at times. Open communication with healthcare providers can ease this burden. Support groups may also help in coping with the journey. Addressing both physical and psychological needs promotes a more comprehensive recovery experience.
What is Nail Intramedullari and How Does it Work? - Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation after Nail Intramedullari Surgery
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Nail Intramedullari is a surgical procedure that involves the insertion of a metal rod into the medullary cavity of a bone to stabilize fractures. |
| Indications | Useful for treating long bone fractures, particularly in the femur and tibia. |
| Procedure Steps | 1. Anesthesia administration 2. Incision and exposure of the bone 3. Insertion of the intramedullary nail 4. Closure of the incision |
| Post-Operative Care | - Pain management - Monitoring for infection - Ensuring proper positioning of the limb |
| Rehabilitation | - Gradual weight-bearing exercises - Physical therapy to restore movement and strength - Follow-up visits for evaluation |
| Expected Outcomes | Successful stabilization of the fracture, improved function, and reduced pain over time. |
