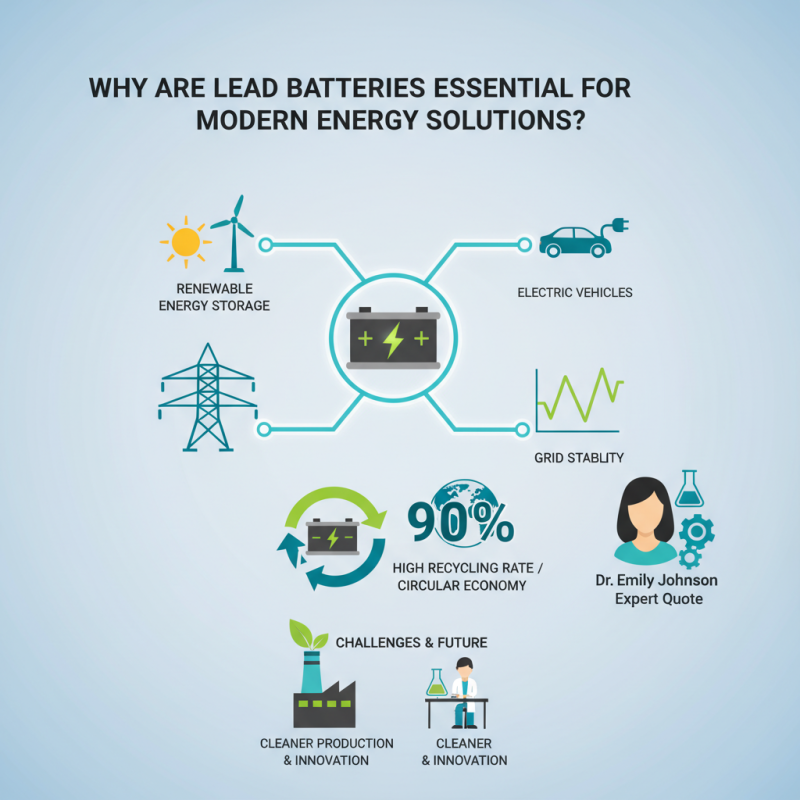
Why Are Lead Batteries Essential for Modern Energy Solutions?
In today's rapidly evolving energy landscape, lead batteries play a crucial role. Their efficiency and reliability make them essential for various applications, from renewable energy storage to electric vehicles. According to a report by the International Battery Association, lead batteries have a 90% recycling rate, highlighting their sustainability. This statistic demonstrates their value in promoting a circular economy.
Dr. Emily Johnson, a renowned expert in battery technology, states, "Lead batteries are not just a choice; they are a necessity for our energy future." This reflects the growing recognition of lead batteries in energy management. They support grid stability and help integrate renewables like solar and wind power into the system.
Yet, challenges remain. Lead battery production must address environmental concerns and the industry's reliance on extraction practices. Research shows that developing cleaner production methods is vital for long-term viability. The continued evolution of lead battery technology is essential, but it requires innovation and commitment from all stakeholders.
Role of Lead Batteries in Renewable Energy Storage Systems

Lead batteries play a vital role in renewable energy storage systems. They store excess energy generated from sources like solar and wind. This process makes renewable energy more reliable and accessible. When the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing, these batteries release energy to meet demand. This ability to stabilize energy supply is crucial for modern grids.
However, lead batteries are not without challenges. They face issues with efficiency and environmental impact. Recycling practices need improvement. There are concerns about lead exposure in certain contexts. Despite these drawbacks, their cost-effectiveness and scalability make them prominent in energy storage. They continue to evolve, with ongoing research aimed at enhancing their performance.
The transition to sustainable energy is complex. Lead batteries offer practical solutions but require responsible management. Balancing their benefits with potential hazards is essential for a sustainable future. As we move forward, it’s important to reflect on how we handle these technologies. The future of energy lies in improving what we already have.
Advantages of Lead Batteries in Energy Management Solutions
Lead batteries play a crucial role in modern energy management solutions. Their standout feature is durability. They can withstand many charge and discharge cycles. This longevity makes them ideal for renewable energy systems, like solar and wind. They store excess energy efficiently, allowing for consistent power supply.
Another advantage is their cost-effectiveness. Lead batteries require less upfront investment compared to other technologies. They are also easy to recycle, reducing environmental impact. Many industries rely on them for backup power. Their reliability during peak demand is undeniable. People often overlook how vital they are in this context.
However, challenges remain. Lead batteries are heavy and require maintenance. Their performance can degrade if not managed properly. It’s essential to address these issues for optimal efficiency. This opens the floor for innovation. Many researchers are exploring ways to improve lead battery technology, ensuring they remain relevant in our evolving energy landscape.
Benefits of Lead Batteries in Energy Management
The chart above illustrates the key advantages of lead batteries in modern energy management solutions, rated on a scale from 1 to 10. Lead batteries are recognized for their cost-effectiveness and recycling efficiency, making them a vital component in sustainable energy systems.
Comparison of Lead Batteries with Alternative Energy Storage Technologies

Lead batteries have long been a cornerstone of energy storage solutions. They offer a remarkable balance of efficiency and reliability. Compared to alternative technologies like lithium-ion or flow batteries, lead batteries are more cost-effective and widely available. According to a report from the Battery Council International, lead batteries have a recycling rate of over 99%. This makes them more sustainable in the long run.
When we look at their lifespan, lead batteries typically last between three to five years in cyclic applications. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries might last longer but come at a higher cost. Furthermore, lead batteries can perform better under high temperature conditions, making them suitable for diverse environments. However, they are heavier and take up more space. This can limit their use in smaller applications.
While lead batteries are essential, they are not without flaws. They require regular maintenance and can be less efficient in energy discharge. Lithium-ion batteries tend to perform better in terms of efficiency. Yet, their environmental impact and recycling challenges raise concerns. As we explore energy storage options, it’s crucial to weigh these pros and cons while considering future energy needs. The industry must innovate to address these gaps in lead battery technology.
Applications of Lead Batteries in Electric Vehicles and Grid Stability
Lead batteries play a crucial role in electric vehicles. They offer high energy density and robust power for quick acceleration. Their design allows for deep cycling, which is essential for stop-and-go driving in urban areas. Additionally, they are cost-effective compared to other battery types. This advantage makes them a preferred choice for many vehicles today.
In terms of grid stability, lead batteries provide essential support. They can store excess energy from renewable sources like solar and wind. This capability helps balance supply and demand on the grid. However, lead batteries come with limitations, such as weight and environmental concerns. Their recycling process is vital for sustainability, yet it needs more improvement. The industry must address these challenges, focusing on innovation and cleaner practices.
Future Trends and Innovations in Lead Battery Technology
Lead batteries are vital for today’s energy solutions, but innovations within this sector are shaping a new future. Recent industry reports highlight that the lead battery market is expected to grow to over $130 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by increasing demand for renewable energy storage. Advanced manufacturing techniques have made lead batteries more efficient and reliable for various applications.
Innovations are emerging. Researchers are exploring new materials to enhance battery performance. For instance, adding nanomaterials can lead to better energy density and lifespan. Some companies are developing recyclable lead batteries that minimize environmental impact. This path forward is not without challenges. The need for better recycling processes remains critical. Studies show that only 50% of used lead batteries are recycled effectively.
Tips: Always check the recycling policies in your area. Choose local facilities that specialize in battery disposal. This can improve recycling rates.
The future is bright, but questions linger. How can we ensure a sustainable supply chain? As technology evolves, continuous monitoring is essential. Innovations may bring solutions, but they require our attention. Understanding these trends is crucial to leveraging lead battery technology effectively.
Why Are Lead Batteries Essential for Modern Energy Solutions? - Future Trends and Innovations in Lead Battery Technology
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Energy Density | Lead batteries have a moderate energy density, typically around 30-40 Wh/kg. |
| Cycle Life | They offer a cycle life ranging from 500 to 1500 cycles, depending on usage. |
| Recycling Rate | Lead batteries have a recycling rate of over 95%, making them very environmentally friendly. |
| Applications | Commonly used in automotive, renewable energy storage, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. |
| Emerging Trends | Innovations include the development of advanced lead-acid battery technologies and hybrid systems. |
Related Posts
-
How to Choose the Right Lead Battery for Your Needs: A Complete Guide
-

Top 10 Facts About Lead Batteries You Need to Know!
-

Unlocking the Benefits: Why Rechargeable Sealed Lead Acid Batteries Are the Future of Power Storage
-

Why Choose Maintenance Free Sealed Lead Acid Battery for Your Power Needs
-

Top 10 Best Batteries: Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Battery for Your Needs
-
Exploring the Future of Battery Technology Innovations Strategies to Enhance Performance and Sustainability
