What is Battery Technology and How Do Batteries Work?
Battery technology plays a critical role in our daily lives. From smartphones to electric vehicles, batteries power modern society. Dr. Emily Carter, a well-respected expert in the battery batteries industry, once stated, “The future of energy storage relies on innovative battery technologies.” Her insights highlight the importance of understanding how batteries function.
Batteries convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. They consist of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. When a battery discharges, ions move between the anode and cathode. This flow generates electrical power to run devices. However, the efficiency and longevity of batteries remain challenges. Current battery capacities often fall short of our growing energy demands.
Despite advances, battery batteries still face issues. Not all battery systems are eco-friendly. The extraction of raw materials raises environmental concerns. Additionally, many batteries degrade over time, affecting performance. Thus, ongoing research is essential. Understanding battery technology is key to developing sustainable solutions and innovative applications.

What is Battery Technology?
Battery technology refers to the science and engineering behind energy storage devices. Understanding how batteries work is crucial in our modern world. Researchers estimate that the global battery market will reach $112 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage solutions.
Batteries operate by converting chemical energy into electrical energy. They contain two electrodes: an anode and a cathode, separated by an electrolyte. When a battery discharges, chemical reactions occur at both electrodes, resulting in the flow of electrons through an external circuit. This process powers electronic devices. Over time, batteries experience deterioration. This degradation can reduce their effectiveness and lifespan, leading to the need for careful management.
Tips: Always charge your battery according to the manufacturer's guidelines. Avoid extreme temperatures, as they can accelerate wear. Many batteries struggle with deep discharge cycles. Charging them regularly can extend their life significantly.
Battery technology is evolving rapidly. Innovations in materials and design are produced daily. Solid-state batteries show promise for safer and more efficient energy storage. However, challenges remain. Cost, scalability, and recycling issues need addressing. The future relies on overcoming these hurdles to make batteries more sustainable.
The Basic Principle of How Batteries Work
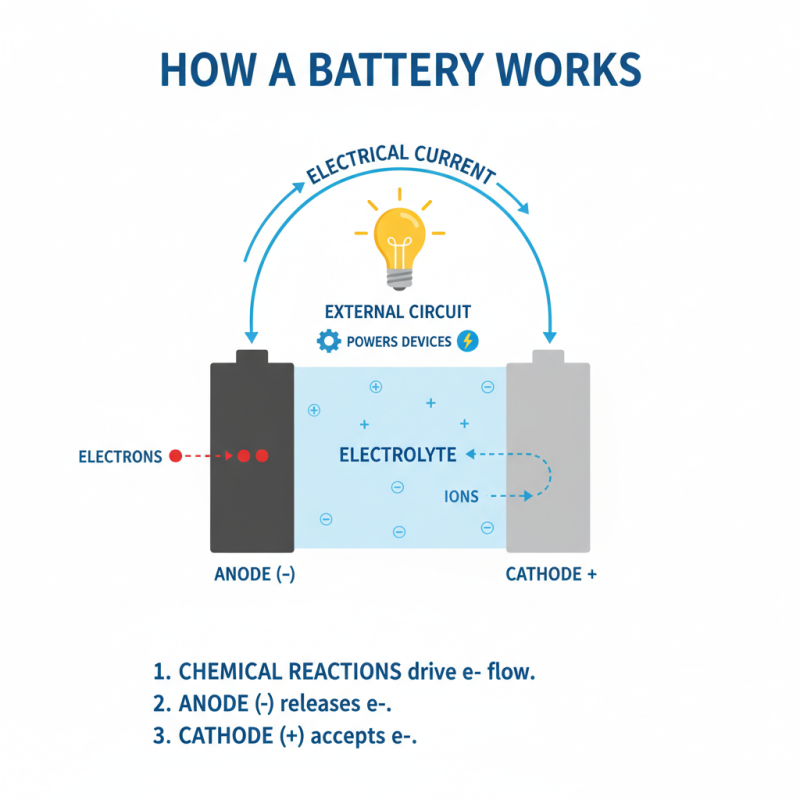
Batteries are essential devices that store energy for various applications. Their basic principle revolves around chemical reactions. These reactions occur between two electrodes: the anode and the cathode. An electrolyte facilitates the movement of ions. When a battery discharges, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit. This generates electric current, which powers devices.
Different battery types utilize various chemicals. Some rely on lithium, while others use lead or alkaline solutions. Each type has unique characteristics, affecting energy density and charging speed. With so many options, choosing the right battery can be challenging. The complexity of battery technology often leaves consumers confused. Misunderstandings about energy capacity and lifespan frequently arise.
Batteries also have limitations. Degradation occurs over time, impacting performance. Environmental factors can speed up this process. Understanding these details is crucial. It helps users make informed decisions. Batteries play a vital role in modern life, but their operation and effectiveness must be considered carefully.
Types of Batteries and Their Applications
Battery technology has evolved significantly, providing various types of batteries for diverse applications. The most common types include lithium-ion, lead-acid, nickel-metal hydride, and alkaline batteries. Each type has unique characteristics suited for different purposes.
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their high energy density and lightweight design. They are widely used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency, lithium-ion battery production capacity is expected to exceed 2,500 GWh by 2030, supporting the growing demand for electric vehicles.
Lead-acid batteries, while older technology, are still relevant. They are often used in automotive starter applications. They are less expensive yet heavier and have a shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion batteries. Nickel-metal hydride batteries find their niche in hybrid electric vehicles, providing a balance between performance and cost.
Tips: When considering battery options, think about energy needs first. Assess the lifespan and the weight of the battery. A heavier battery might be less convenient. Always look for recycling options, as many batteries contain materials that can be harmful if not disposed of correctly.
Key Components of a Battery System
Understanding the key components of a battery system is essential. A battery is made of several parts that work together. The most crucial elements are the anode, cathode, and electrolyte.
The anode is where the oxidation occurs. It loses electrons during the discharge process. The cathode, on the other hand, is where reduction happens. Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit. This flow generates electrical energy, powering our devices. It’s interesting to note that the choice of materials affects the battery's overall performance.
The electrolyte is another key player. It facilitates the movement of ions between the anode and cathode. A liquid, gel, or solid can serve as an electrolyte. Each type has its advantages and challenges. For instance, a liquid electrolyte can offer high conductivity. Yet, it may pose leakage risks. Balancing these aspects is a constant challenge in battery design.
What is Battery Technology and How Do Batteries Work? - Key Components of a Battery System
| Component | Function | Material | Typical Voltage Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anode | Serves as the source of electrons | Graphite | 3.0 - 4.2 V |
| Cathode | Acts as the electron acceptor | Lithium Cobalt Oxide | 3.0 - 4.5 V |
| Electrolyte | Facilitates ionic movement | Lithium Salt in Organic Solvent | N/A |
| Separator | Prevents short-circuiting | Polyethylene | N/A |
| Current Collectors | Conducts electrical current | Copper and Aluminum | N/A |
Future Trends in Battery Technology and Innovation
Battery technology is rapidly evolving. New developments focus on improving efficiency and sustainability. One exciting trend is the use of solid-state batteries. These batteries offer higher energy density and enhanced safety. They could potentially replace traditional lithium-ion batteries, but challenges remain. Manufacturing processes need to be refined. Costs must come down to encourage widespread adoption.
Another area of innovation is recycling. As battery use grows, so does the need for sustainable disposal methods. Companies are exploring how to reclaim valuable materials from old batteries. This could reduce environmental impact. However, the technology and logistics of recycling are still in their infancy. Developing effective methods will require significant investment and research.
Advancements in battery charging technology are also noteworthy. Ultra-fast charging stations are beginning to emerge. These could allow for quick turnaround times for electric vehicles. Yet, questions linger about infrastructure capabilities. Widespread deployment still faces hurdles. It’s clear that while the future of battery technology is promising, many challenges lie ahead. Solutions will require collaboration across industries and continuous innovation.
Related Posts
-

Why Do We Need Different Types of Battery and Batteries?
-

Unleashing the Power: Exploring the Future of Eco-Friendly Batteries & More Innovations
-

How to Choose the Best Battery for Your Needs in 2025
-

What is an AGM Lawn Mower Battery and How Does It Work
-

2025 Top 5 Lawnmower Batteries for Optimal Performance and Longevity You Can't Miss
-

Batteries Delivered Revolutionizing Supply Chains at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
